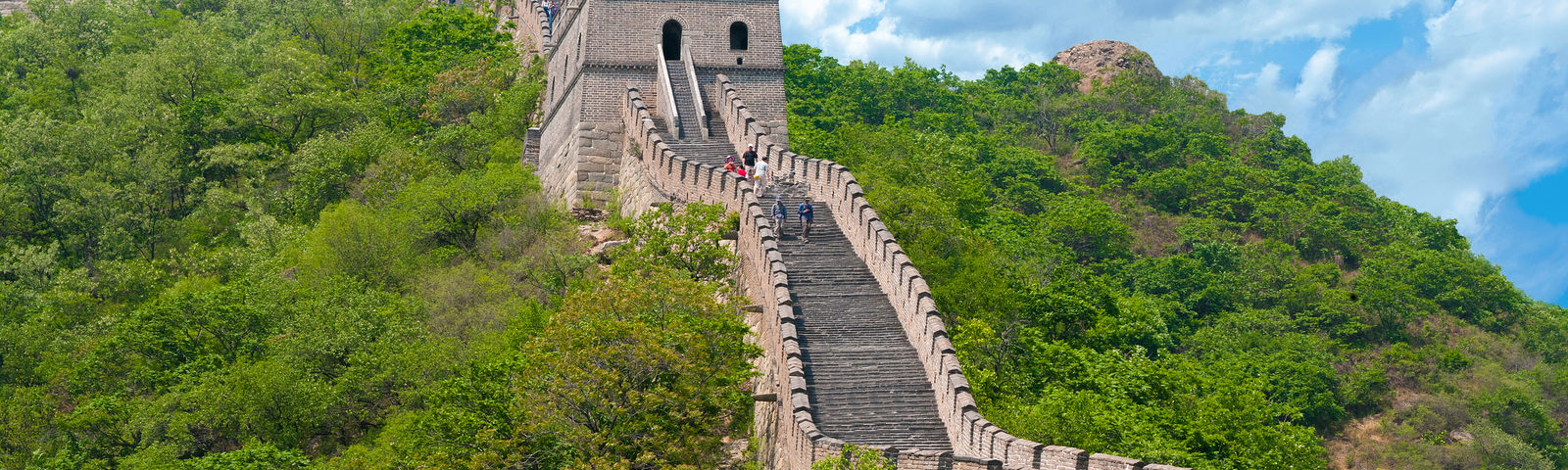
Top picks for Beijing Day tours
Discover 689 Day tours in Beijing on Trip.com, updated January 31, 2026, with experiences lasting from 1 to 14 hours. Find the perfect adventure for your day!
From EUR 6.13 per person, with an average total of EUR 46.42. Choose the option that suits your plan.
With 50.673k verified reviews, Day tours Beijing boast an average rating of 4.9.
This week's most popular Day tours: "A one-day tour of the Palace Museum in Beijing [Pre-sale for Chinese New Year, including admission | Detailed lectures by a scholar | Gift of precious artifacts]", with 25.895k reviews and a 4.9 rating.
Now on Trip.com: "Temple of Heaven, Lama Temple, Summer Palace & Peking Duck One Day Bus Tour", a 7-hour adventure in Beijing!
The next available day tour departs on February 1, 2026. Book now to secure your spot!
Beijing Day tours usually take about 7 hours — perfect for a relaxed, immersive experience!
97% of Beijing Day tours now offer English-speaking guides
January is the perfect time to visit Beijing! Choose from Day tours available day tours, including seasonal favorites like A one-day tour of the Palace Museum in Beijing [Pre-sale for Chinese New Year, including admission | Detailed lectures by a scholar | Gift of precious artifacts].
Your trip, worry-free! All day tours are run by licensed suppliers with verified reviews, and many include free cancellation before departure.
689 results for Beijing Day tours
 Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 7.6 hrsEnglish4.8/5Very good· 32 reviews· 310 booked10% offLimited-time saleFrom€43.55€48.39
Duration: 7.6 hrsEnglish4.8/5Very good· 32 reviews· 310 booked10% offLimited-time saleFrom€43.55€48.39 Duration: 13.7 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 14 reviews· 86 bookedFrom€50.06
Duration: 13.7 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 14 reviews· 86 bookedFrom€50.06 Duration: 8.1 hrsEnglish5.0/5Excellent· 1 review10% offLimited-time saleFrom€70.55€78.39
Duration: 8.1 hrsEnglish5.0/5Excellent· 1 review10% offLimited-time saleFrom€70.55€78.39 Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 3.6 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 813 reviews· 5.1k bookedSave 1.8Limited-time saleFrom€34.25€36.05
Duration: 3.6 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 813 reviews· 5.1k bookedSave 1.8Limited-time saleFrom€34.25€36.05![Temple of Heaven Family Study Half-Day Tour [Includes Combo Ticket + Study Guide]|Snail Cultural Tourism Fun Interactive Experience](https://ak-d.tripcdn.com/images//0582y12000n0hdpi27E5D_C_568_320.jpg?_fr=wc) Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 4 hrsEnglish5.0/5Excellent· 12 reviews· 147 booked5% offLimited-time saleFrom€147.10€154.85
Duration: 4 hrsEnglish5.0/5Excellent· 12 reviews· 147 booked5% offLimited-time saleFrom€147.10€154.85 Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 5.3 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 17 reviews· 118 booked5% offLimited-time saleFrom€342.47€360.5
Duration: 5.3 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 17 reviews· 118 booked5% offLimited-time saleFrom€342.47€360.5 Duration: 11.4 hrsEnglish5.0/5Excellent· 1 reviewFrom€41.72
Duration: 11.4 hrsEnglish5.0/5Excellent· 1 reviewFrom€41.72![Beijing Temple of Heaven Half-Day Tour [Combined Ticket Available in Chinese, English, and Multilingual Packages]](https://ak-d.tripcdn.com/images/0355w12000pnj6tfgABD3_C_568_320.jpg?_fr=wc) Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 2 hrsEnglish5.0/5Excellent· 5 reviews10% offLimited-time saleFrom€43.11€47.91
Duration: 2 hrsEnglish5.0/5Excellent· 5 reviews10% offLimited-time saleFrom€43.11€47.91 Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 7.5 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 101 reviews· 927 bookedFrom€28.80
Duration: 7.5 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 101 reviews· 927 bookedFrom€28.80 Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 8.7 hrsEnglish4.7/5Very good· 21 reviews· 150 bookedFrom€25.17
Duration: 8.7 hrsEnglish4.7/5Very good· 21 reviews· 150 bookedFrom€25.17 Duration: 9.7 hrsEnglish5.0/5Excellent· 1 reviewFrom€41.72
Duration: 9.7 hrsEnglish5.0/5Excellent· 1 reviewFrom€41.72![Beijing Temple of Heaven + Summer Palace + Yuanmingyuan Park 1-day tour [Professional guide, sincere service]](https://ak-d.tripcdn.com/images/10041f000001gp8md42BC_C_568_320.jpg?_fr=wc) Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 5.2 hrsEnglish4.5/5Satisfied· 6 reviews· 100 bookedFrom€62.43
Duration: 5.2 hrsEnglish4.5/5Satisfied· 6 reviews· 100 bookedFrom€62.43![Beijing Temple of Heaven half-day tour [Snail Travel] Hall of Prayer for Good Harvests + Yuanqiutan + Echo Wall](https://ak-d.tripcdn.com/images/0355s12000o0pjmrd7565_C_568_320.jpg?_fr=wc) Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 3.9 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 136 reviews· 1.5k bookedSave 1.8Limited-time saleFrom€34.25€36.05
Duration: 3.9 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 136 reviews· 1.5k bookedSave 1.8Limited-time saleFrom€34.25€36.05 Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 9 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 16 reviews· 143 booked5% offLimited-time saleFrom€65.28€68.72
Duration: 9 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 16 reviews· 143 booked5% offLimited-time saleFrom€65.28€68.72![[Optional 25-person group] Comprehensive one-day tour of Tiananmen Square, the Forbidden City, and the Temple of Heaven.](https://ak-d.tripcdn.com/images/0355112000qs7ohf4043C_C_568_320.jpg?_fr=wc) Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 6 hrsEnglish4.8/5Very good· 149 reviews· 2.3k bookedFrom€67.51
Duration: 6 hrsEnglish4.8/5Very good· 149 reviews· 2.3k bookedFrom€67.51![Beijing Tiananmen Square + Forbidden City + Temple of Heaven 1-day tour [Optional with pickup/boutique group/private group]](https://ak-d.tripcdn.com/images//0586f12000pa33qkl8306_C_568_320.jpg?_fr=wc) Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 6.2 hrsEnglish5.0/5Excellent· 28 reviews· 480 bookedFrom€240.50
Duration: 6.2 hrsEnglish5.0/5Excellent· 28 reviews· 480 bookedFrom€240.50![Beijing Temple of Heaven + Tiananmen Square Half-Day Tour Activity [Including Admission Ticket ◆ Guided Tour]](https://ak-d.tripcdn.com/images/0350l12000pqajd8m397B_C_568_320.jpg?_fr=wc) Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 3 hrsEnglish5.0/5Excellent· 13 reviews· 176 bookedFrom€49.36
Duration: 3 hrsEnglish5.0/5Excellent· 13 reviews· 176 bookedFrom€49.36![A one-day tour of the Palace Museum in Beijing [Pre-sale for Chinese New Year, including admission | Detailed lectures by a scholar | Gift of precious artifacts]](https://ak-d.tripcdn.com/images/0102h1200087d62rxDD6F_C_568_320.jpg?_fr=wc) Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 7.4 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 25.9k reviews· 65.1k bookedFrom€36.05
Duration: 7.4 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 25.9k reviews· 65.1k bookedFrom€36.05 Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 4.8 hrsEnglish4.8/5Very good· 914 reviews· 8.9k booked25% offLimited-time saleFrom€23.59€31.46
Duration: 4.8 hrsEnglish4.8/5Very good· 914 reviews· 8.9k booked25% offLimited-time saleFrom€23.59€31.46![[Optional pick-up service] Comprehensive one-day tour of Badaling Great Wall + Summer Palace + Yuanmingyuan Park](https://ak-d.tripcdn.com/images/0353i12000rbga3egF452_C_568_320.png?_fr=wc) Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 9.4 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 839 reviews· 4.7k bookedFrom€60.25
Duration: 9.4 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 839 reviews· 4.7k bookedFrom€60.25 Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 14 hrsEnglish4.8/5Very good· 146 reviews· 796 booked5% offLimited-time saleFrom€32.18€33.88
Duration: 14 hrsEnglish4.8/5Very good· 146 reviews· 796 booked5% offLimited-time saleFrom€32.18€33.88![Half-Day Tour of the Beijing Forbidden City [Including Tickets and Free Treasure Hall Ticket] Multiple Group Types / Chinese/English Guided Tour](https://ak-d.tripcdn.com/images/0352012000nxucp0a0693_C_568_320.jpg?_fr=wc) Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 5.9 hrsEnglish4.8/5Very good· 403 reviews· 5.4k booked5% offLimited-time saleFrom€19.31€20.33
Duration: 5.9 hrsEnglish4.8/5Very good· 403 reviews· 5.4k booked5% offLimited-time saleFrom€19.31€20.33 Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 5.7 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 1.5k reviews· 11.1k booked5% offLimited-time saleFrom€15.86€16.7
Duration: 5.7 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 1.5k reviews· 11.1k booked5% offLimited-time saleFrom€15.86€16.7![Mutianyu Great Wal 1-day Tour [Optional Experience of Hutong folk culture & A tour of life and culture in Beijing]](https://ak-d.tripcdn.com/images/0351p12000rb0b72g7A85_C_568_320.jpg?_fr=wc) Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 7.1 hrsEnglish5.0/5Excellent· 137 reviews· 856 booked5% offLimited-time saleFrom€13.56€14.28
Duration: 7.1 hrsEnglish5.0/5Excellent· 137 reviews· 856 booked5% offLimited-time saleFrom€13.56€14.28 Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 7 hrsEnglish5.0/5Excellent· 5 reviews· 26 bookedFrom€19.12
Duration: 7 hrsEnglish5.0/5Excellent· 5 reviews· 26 bookedFrom€19.12 Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 9.5 hrsEnglish4.7/5Very good· 239 reviews· 3.1k bookedFrom€15.67
Duration: 9.5 hrsEnglish4.7/5Very good· 239 reviews· 3.1k bookedFrom€15.67 Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 9 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 5.3k reviews· 15.2k booked5% offLimited-time saleFrom€13.95€14.69
Duration: 9 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 5.3k reviews· 15.2k booked5% offLimited-time saleFrom€13.95€14.69 Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 8.4 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 6.1k reviews· 25.3k bookedFrom€14.45
Duration: 8.4 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 6.1k reviews· 25.3k bookedFrom€14.45 Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 3 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 38 reviews· 507 bookedFrom€6.13
Duration: 3 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 38 reviews· 507 bookedFrom€6.13![Mutianyu Great Wall + Summer Palace 1-day tour [Daily departure at 7:30 AM] Return ends at Bird's Nest](https://ak-d.tripcdn.com/images/0352c12000o5jb50eDF26_C_568_320.jpg?_fr=wc) Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 10.3 hrsEnglish4.8/5Very good· 286 reviews· 3.4k bookedFrom€20.81
Duration: 10.3 hrsEnglish4.8/5Very good· 286 reviews· 3.4k bookedFrom€20.81 Duration: 3–4 hrs4.8/5Very good· 1.6k reviews· 15.3k bookedFrom€8.51
Duration: 3–4 hrs4.8/5Very good· 1.6k reviews· 15.3k bookedFrom€8.51 Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 10 hrsEnglish4.8/5Very good· 74 reviews· 1.2k bookedFrom€16.90
Duration: 10 hrsEnglish4.8/5Very good· 74 reviews· 1.2k bookedFrom€16.90 Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 4.1 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 798 reviews· 806 bookedFrom€28.43
Duration: 4.1 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 798 reviews· 806 bookedFrom€28.43 Duration: 1–4 hrsEnglish4.5/5Satisfied· 236 reviews· 3.9k bookedFrom€6.72
Duration: 1–4 hrsEnglish4.5/5Satisfied· 236 reviews· 3.9k bookedFrom€6.72 Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 11 hrsEnglish4.8/5Very good· 145 reviews· 1.7k bookedFrom€16.90
Duration: 11 hrsEnglish4.8/5Very good· 145 reviews· 1.7k bookedFrom€16.90 Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 4 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 46 reviews· 312 booked18% offLimited-time saleFrom€24.80€30.25
Duration: 4 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 46 reviews· 312 booked18% offLimited-time saleFrom€24.80€30.25![Mutianyu Great Wall Day Trip [Bus service from 7 AM to 12 PM + 5-hour sightseeing tour + no shopping]](https://ak-d.tripcdn.com/images/0355w12000o20mq5xAB8E_C_568_320.png?_fr=wc) Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 8.6 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 4.1k reviews· 30.6k booked8% offLimited-time saleFrom€13.29€14.45
Duration: 8.6 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 4.1k reviews· 30.6k booked8% offLimited-time saleFrom€13.29€14.45![Beijing Gubei Water Town Day Tour [Visit Jiangnan Town/Enjoy Water Town Night View/Independent Tour Available]](https://ak-d.tripcdn.com/images/0355n12000pbnjw8v0501_C_568_320.jpg?_fr=wc) Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 13.1 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 222 reviews· 2k bookedFrom€12.00
Duration: 13.1 hrsEnglish4.9/5Excellent· 222 reviews· 2k bookedFrom€12.00 Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 3.8 hrsEnglish4.8/5Very good· 110 reviews· 1.3k booked15% offLimited-time saleFrom€27.05€31.83
Duration: 3.8 hrsEnglish4.8/5Very good· 110 reviews· 1.3k booked15% offLimited-time saleFrom€27.05€31.83 Trip.Select
Trip.Select Duration: 11.5 hrsEnglish4.8/5Very good· 126 reviews· 1.6k booked5% offLimited-time saleFrom€23.26€24.49
Duration: 11.5 hrsEnglish4.8/5Very good· 126 reviews· 1.6k booked5% offLimited-time saleFrom€23.26€24.49
Explore top experiences
See what other travellers love, based on ratings and bookings
Frequently asked questions about Beijing Day tours
How many Day tours are available in Beijing on Trip.com?
What are the best Day tours in Beijing?
What are the top-rated Day tours in Beijing?
What are the recommended itineraries in Beijing?
How can I contact Trip.com customer support?
Can I change or cancel my booking?
How can I get discounted prices?
Reviews/Trip Moments
Trip.com Picks
Popular Beijing Tours
Best Beijing Experiences
Popular Products
Popular Activities
About





of the year 2025
Site Operator: Trip.com Travel Singapore Pte. Ltd.